Introduction
Gaza, often referred to as the Gaza Strip, is a narrow piece of land along the Mediterranean coast. It has been a focal point of historical, political, and humanitarian interest for decades. This blog delves into the geography, population, and various aspects of life in Gaza.
Geography and Location
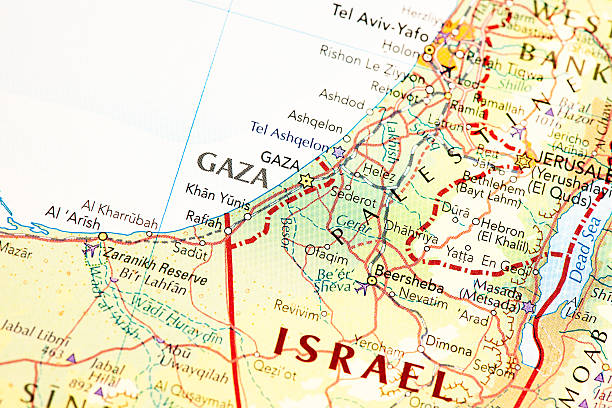
Gaza is situated on the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea, bordered by Egypt to the southwest and Israel on the north and east. It covers an area of about 365 square kilometers (141 square miles). The region is part of the Palestinian territories and is one of the most densely populated areas in the world. Its strategic location has made it a significant spot in historical and modern geopolitical contexts.
Population
As of the latest estimates, Gaza is home to approximately 2 million people. The population density is incredibly high, with over 5,000 people per square kilometer. The majority of the inhabitants are Palestinian Arabs, and a significant portion of the population are refugees who were displaced during the 1948 Arab-Israeli War and their descendants.
History and Significance
Gaza has a rich history that dates back to ancient times. It has been inhabited for over 5,000 years and has seen the rise and fall of numerous civilizations, including the Egyptians, Philistines, and Romans. In modern history, Gaza has been a focal point in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, with its control and governance frequently changing hands.
Governance
Since 2007, Gaza has been governed by Hamas, an Islamist political organization. The governance of Gaza has been a contentious issue, leading to various conflicts and a blockade imposed by Israel and Egypt. This blockade has significantly impacted the living conditions and economy of the region.
Economy
The economy of Gaza is primarily based on agriculture, fishing, and small-scale industries. However, the blockade and recurring conflicts have severely hampered economic activities. Unemployment rates are exceedingly high, and many families live below the poverty line. International aid plays a crucial role in sustaining the population.
Daily Life
Life in Gaza is marked by a mix of resilience and challenges. The blockade has led to shortages of essential goods, including food, medical supplies, and construction materials. Despite these hardships, the people of Gaza have developed a strong sense of community and perseverance. Education is highly valued, and many young Gazans pursue higher education, often with the hope of finding opportunities abroad.
Education
Education is a vital part of Gazan society. There are numerous schools and universities, including the Islamic University of Gaza and Al-Azhar University – Gaza. However, the educational sector faces challenges such as damaged infrastructure and limited resources due to the blockade.
Health Care
The healthcare system in Gaza is under tremendous strain. Hospitals and clinics often operate with limited supplies and equipment. Frequent power outages and the blockade further complicate the delivery of healthcare services. Despite these obstacles, medical professionals in Gaza continue to provide care under difficult circumstances.
Humanitarian Aid
International organizations, including the United Nations Relief and Works Agency (UNRWA), provide essential support to the people of Gaza. This aid includes food assistance, healthcare, and educational support. Humanitarian efforts are crucial in alleviating some of the hardships faced by Gazans.
Cultural Life
Gaza has a rich cultural heritage that includes traditional music, dance, and crafts. Despite the challenges, cultural activities and events are an integral part of life in Gaza. The people celebrate various festivals and maintain their traditions, contributing to a strong sense of identity and community.
Conclusion
Gaza is a region of significant historical and geopolitical importance, marked by resilience in the face of adversity. The people of Gaza continue to navigate the complexities of daily life amid economic challenges, political conflict, and a blockade. Understanding Gaza requires acknowledging its rich history, the strength of its people, and the ongoing efforts to improve living conditions through education, healthcare, and international aid.